Eurostat News Release: At risk of poverty or social exclusion in the EU28 – More than 120 million persons at risk of poverty or social exclusion in 2013 – Almost 1 out of every 4 persons in the EU in this situation, 04 Νοεμβρίου.
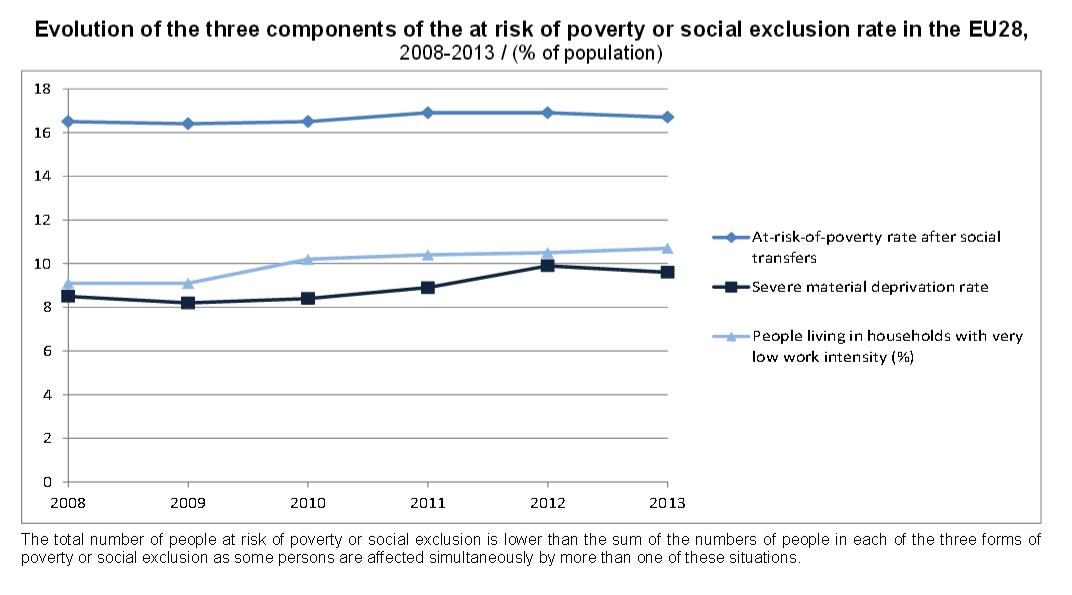
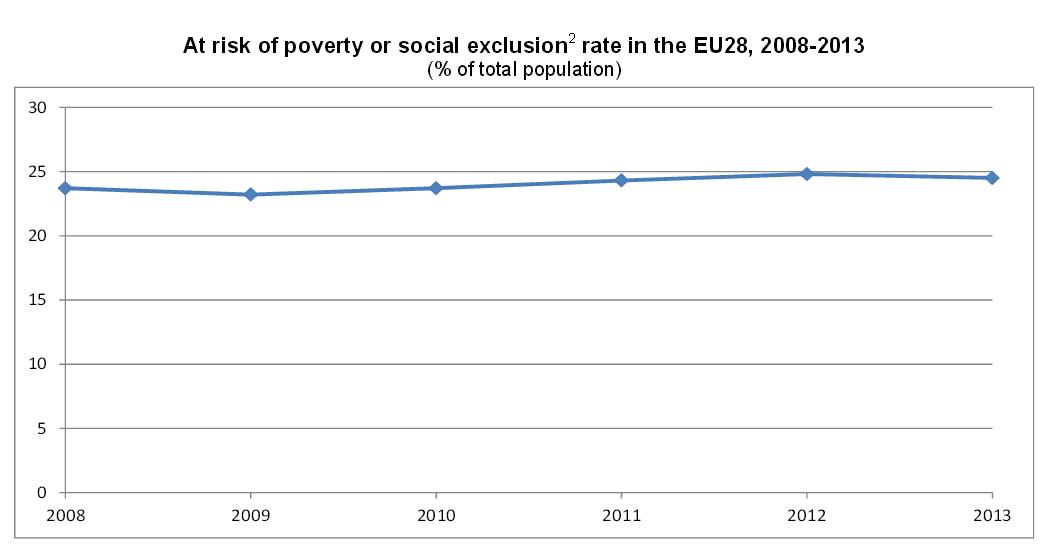
In 2013, 122.6 million people, or 24.5% of the population, in the EU were at risk of poverty or social exclusion. This means that these people were in at least one of the following three conditions: at-risk-of-poverty after social transfers (income poverty), severely materially deprived or living in households with very low work intensity. The proportion of persons at risk of poverty or social exclusion in the EU28 in 2013 (24.5%) has slightly decreased compared with 2012 (24.8%), but is higher than in 2008 (23.8%). The reduction of the number of persons at risk of poverty or social exclusion in the EU is one of the key targets of the Europe 2020 strategy.
These figures are published by Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union and are based on data from the EU-SILC survey.
Highest at risk of poverty or social exclusion rate in Bulgaria, lowest in the Czech Republic
In 2013, more than a third of the population was at risk of poverty or social exclusion in five Member States: Bulgaria (48.0%), Romania (40.4%), Greece (35.7%), Latvia (35.1%) and Hungary (33.5%). On the contrary, the lowest shares of persons being at risk of poverty or social exclusion were recorded in the Czech Republic (14.6%), the Netherlands (15.9%), Finland (16.0%) and Sweden (16.4%).
Among Member States for which data are available, the at-risk-of-poverty or social exclusion rate has increased from 2008 to 2013 in most of the Member States, the only decreases being recorded in Poland (from 30.5% in 2008 to 25.8% in 2013), Romania (from 44.2% to 40.4%), Austria (from 20.6% to 18.8%), Finland (from 17.4% to 16.0%), Slovakia (from 20.6% to 19.8%), the Czech Republic (from 15.3% to 14.6%) and France (from 18.5% to 18.1%), while the share remained stable in Belgium.