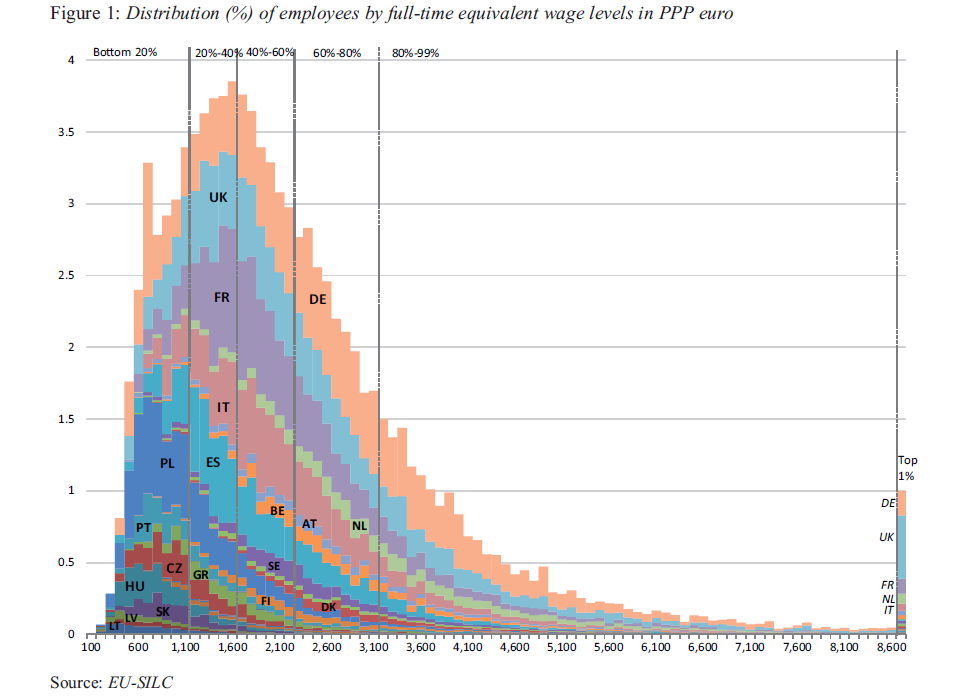
According to the analysis, the level of wage inequality in the EU as a whole is below that of the US and the three most unequal countries in the EU – Latvia, Portugal and the UK – when wages are measured in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). The Gini index for wages in the EU as a whole is 0.346 (for full-time equivalent wages measured in PPP), while the comparable measure for the US is around 0.4, and in the UK, the most unequal EU country, it is 0.404. The majority of EU countries have Gini values for full-time equivalent wages well below the
overall EU figure.
The Great Recession changed the trend of overall EU wage inequality, with wage inequality levels decreasing in the period 2004 and 2008 and subsequently increasing. This decrease before the crisis was due to a process of convergence in pay levels between countries which stopped in 2008 and was starting to reverse in 2011, the end of the period of analysis for this report. The main driver behind the increase in wage inequality after 2008 was withincountry inequality, which in the earlier period had remained more or less stable in many countries.
Eurofound (2015), “Recent developments in the distribution of wages in Europe”, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg.
Σχετικές Αναρτήσεις
OECD (2015), FOCUS on Minimum Wages after the crisis, OECD Directorate for Employment, Labour and Social Affairs, Mάιος 2015